Dementia is more than just occasional forgetfulness—it’s a serious group of conditions that affects millions of individuals and their families worldwide. While dementia is typically age-related and sets in after 65, it could develop in adults as young as 30 or 40 in early onset dementia. Understanding dementia, its early signs, and how it impacts lives can make all the difference in managing and potentially mitigating its effects.
Equipping yourself and your loved one with the knowledge of dementia can also help in future plans. For example, you can explore future senior care options like memory care if there is a known increased risk of dementia or one of its related conditions.
Understanding Dementia
Dementia is an umbrella term used to describe a range of neurological disorders characterized by a decline in cognitive function severe enough to interfere with daily life. It’s not a single disease but a collection of symptoms associated with various conditions.
Common types of dementia include Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia. Each type has unique characteristics, but they all share the common thread of impacting memory, thinking, and behavior.
Early Signs to Look Out For
Recognizing the early signs of dementia can be challenging, as they often develop gradually and might be mistaken for normal aging. Key early indicators include:
- Memory loss, especially short-term memory
- Difficulty with problem-solving or planning
- Confusion about time or place
- Trouble understanding visual images and spatial relationships
- Problems with speaking or writing
- Withdrawal from social activities
- Changes in mood or personality
Early-Onset Dementia
Early-onset dementia refers to dementia diagnosed in individuals younger than 65. Though less common, it can occur in people in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. This form of dementia is often misdiagnosed due to its rarity and the tendency to attribute symptoms to stress or mental health issues.
An important thing to remember about dementia—regardless of whether early-onset or not—is that aging is a risk factor, not a cause. Dementia is not an inevitable part of growing older.
Factors Influencing Onset
There isn’t a black-and-white answer for what causes dementia because researchers still don’t know the exact cause. However, the following factors can influence its onset.
Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in the onset of some types of dementia. For example, familial Alzheimer’s disease is linked to specific genetic mutations and typically presents symptoms before 65. If you have a family history of dementia, discussing it with a healthcare professional can provide insight into your potential risks.
External & Internal Factors
Environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and overall health also influence the onset of dementia. Medical conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and smoking can increase the risk. Head injuries and prolonged exposure to toxins may contribute to the development of dementia-related conditions.
Early Detection & Intervention
Dementia—especially early-onset dementia—can be misdiagnosed as a normal part of aging in the early stages when there’s only mild memory loss.
Importance of Recognizing Symptoms Early
Early detection of dementia can make a significant difference in managing the disease. Recognizing symptoms early allows individuals to seek medical advice, explore treatment options, and plan for the future.
Treatment & Support
While there is no cure for dementia, treatments are available to help manage symptoms. Medications can slow the progression of certain types of dementia, and non-pharmacological interventions, like cognitive therapies, can improve quality of life. Support groups and resources for patients and caregivers provide essential emotional support and practical assistance.
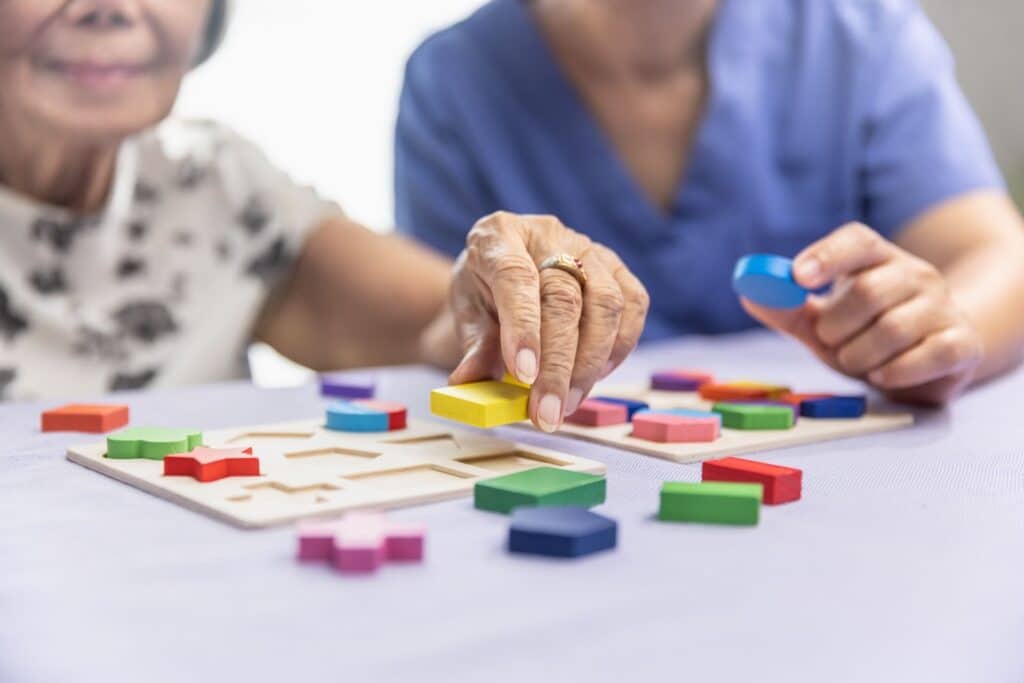

Lifestyle Choices & Prevention
It may not always be possible to prevent dementia. But there are things we can do to lessen the risk.
Maintaining Brain Health
Making healthy lifestyle choices can reduce the risk of developing dementia. Recommendations include:
- Regular physical exercise
- A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Mental stimulation through puzzles, reading, and learning new skills
- Social engagement with family, friends, and community activities
- Managing cardiovascular health through regular check-ups and maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels
Reducing Risk Factors
Avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and ensuring adequate sleep are also vital in maintaining brain health. Protective measures like wearing helmets during activities that pose a risk of head injury are equally important.
The Role of Caregivers
Caregivers play a crucial role in the support system for individuals with dementia. Their responsibilities can be physically and emotionally demanding, often requiring significant adjustments in their own lives.
There are often challenges such as managing behavioral changes, balancing work and caregiving duties, and dealing with their feelings of grief and loss. Support networks, both formal and informal, are essential in providing caregivers with the help they need.
Plan for the Future with Us
Understanding dementia and its onset is crucial for early detection, effective management, and improving the quality of life for those affected. Staying informed, making healthy lifestyle choices, and fostering strong support networks are all ways we can collectively create a compassionate and prepared community.
A dementia diagnosis can complicate a senior’s and their family’s lives. But, there are senior lifestyle options like memory care and specialty services like respite care that can minimize or eliminate some of these potential complications.
Call our team at The Legacy at Cimarron today to book a community tour. We’re happy to show you the quality of life you can expect when you call our community home.