Insomnia can have you staring at the ceiling, wondering why sleep is so elusive. For many older adults, insomnia is a common yet often overlooked issue that can impact daily lives, health, and overall well-being.
Causes of insomnia in older adults can include:
- Age-related changes
- Medical conditions
- Medications
- Psychological factors
- Lifestyle factors
- Environmental factors
In senior living communities, coordinated efforts with healthcare professionals and services like medication management can help.
What Is Insomnia?
Insomnia isn’t just about tossing and turning at night. It’s a complex sleep disorder that can disrupt the quality of life. In older adults, insomnia can include difficulty falling asleep, frequent waking during the night, or waking up too early. Insomnia can also cause poor-quality sleep, making you feel tired when you wake up.
Insomnia can be categorized into two types based on time:
- Acute Insomnia: Short-term and often triggered by stress or life changes, and can last for a few days or weeks
- Chronic Insomnia: Long-term and occurs at least 3 nights a week for 3 months or more
Causes of Insomnia in Seniors
Recognizing insomnia symptoms and determining the underlying cause is crucial for finding the right approach to treatment.
Age-Related Changes
As we age, our bodies undergo several changes that affect the quality of our sleep. The circadian rhythm, which regulates the sleep-wake cycle, tends to shift, causing older adults to feel sleepy earlier in the evening and wake up earlier in the morning.
Medical Conditions
Medical conditions like arthritis, diabetes, and heart disease can contribute to sleep disturbances. Pain, discomfort, and the frequent need to use the bathroom at night can make it challenging to get a good night’s rest.
Sleep apnea, a condition where breathing stops and starts repeatedly during sleep, is also more common in older adults. While these are two different conditions, sleep apnea can cause sleep anxiety and cause acute insomnia.
Medications
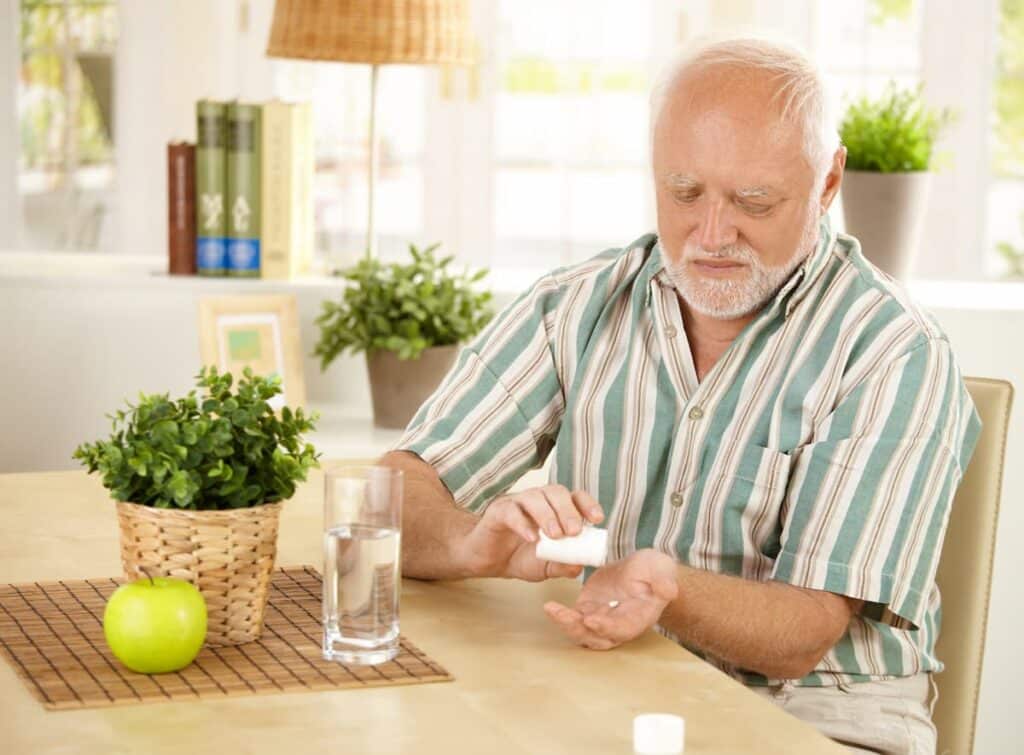

Older adults who take multiple medications for various health conditions can experience insomnia. Medications like antidepressants and antihistamines can interfere with sleep patterns. Substances like alcohol and caffeine can also affect sleep. It’s essential to review medications with a healthcare provider to identify any potential sleep-disrupting side effects.
Psychological Factors
Mental health plays a significant role in sleep quality. Anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline can all contribute to insomnia. The stress of life changes, such as retirement or the loss of a loved one, can also exacerbate sleep problems.
Lifestyle Choices
Certain habits and routines can hinder sleep. Lack of physical activity, excessive daytime napping, and irregular sleep schedules from shift work can all contribute to insomnia. Additionally, too much time spent using electronic devices before bed can interfere with the body’s natural sleep signals.
Environmental Factors
The sleep environment itself can impact sleep quality. Too much noise or light can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. Sometimes, when moving to a new home, the lack of comfort and familiarity with the place can negatively impact sleep.
The Role of Caregivers & Family Support
Caregivers and family members play a crucial role in supporting loved ones with insomnia. Here are some ways to help.
Identifying Sleep Problems
Pay attention to any signs of sleep disturbances, such as frequent waking, daytime fatigue, or irritability. Encourage open communication about sleep issues and reassure them that it’s okay to seek help.
Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Make the bedroom a proper place for sleeping. Use blackout curtains to block out light, keep the room cool and quiet, and invest in a comfortable bed. Removing electronic devices from the bedroom can also help reduce distractions at night.
Establish Routines
Consistency is key to good sleep. Encourage a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day. Develop a relaxing bedtime routine that includes activities like reading or listening to calming music.
Treatment & Healthy Sleep Practices for Seniors
Treatment and healthy sleep practices can help prevent sleep loss and reduce daytime symptoms.
Daily Exercise
Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality. Aim for at least 20 minutes of moderate exercise most days, but avoid vigorous activity close to bedtime.
Diet & Nutrition
Be mindful of what you eat and drink. Avoid large meals, caffeine, and alcohol in the hours leading up to bedtime. A light snack can sometimes help promote sleep.
Lifestyle Changes
You should also avoid napping in the middle of the day. Talk to your healthcare provider if you suspect certain medications are causing insomnia.
Establishing a routine and a regular sleep schedule can also lead to higher-quality sleep,
Seeking Professional Help
If sleep problems persist, it’s important to seek help from a healthcare provider. They can identify underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatments or medication adjustments.
While insomnia is common in older adults, it’s often manageable with the right support and lifestyle adjustments. By understanding the causes, creating a supportive environment, and adopting healthy sleep practices, older adults can enjoy restful nights and improved overall well-being.
If a loved one is struggling with insomnia, don’t hesitate to seek help. Contact our team at The Legacy at Long Meadow to learn more about how we can support you and your loved one.